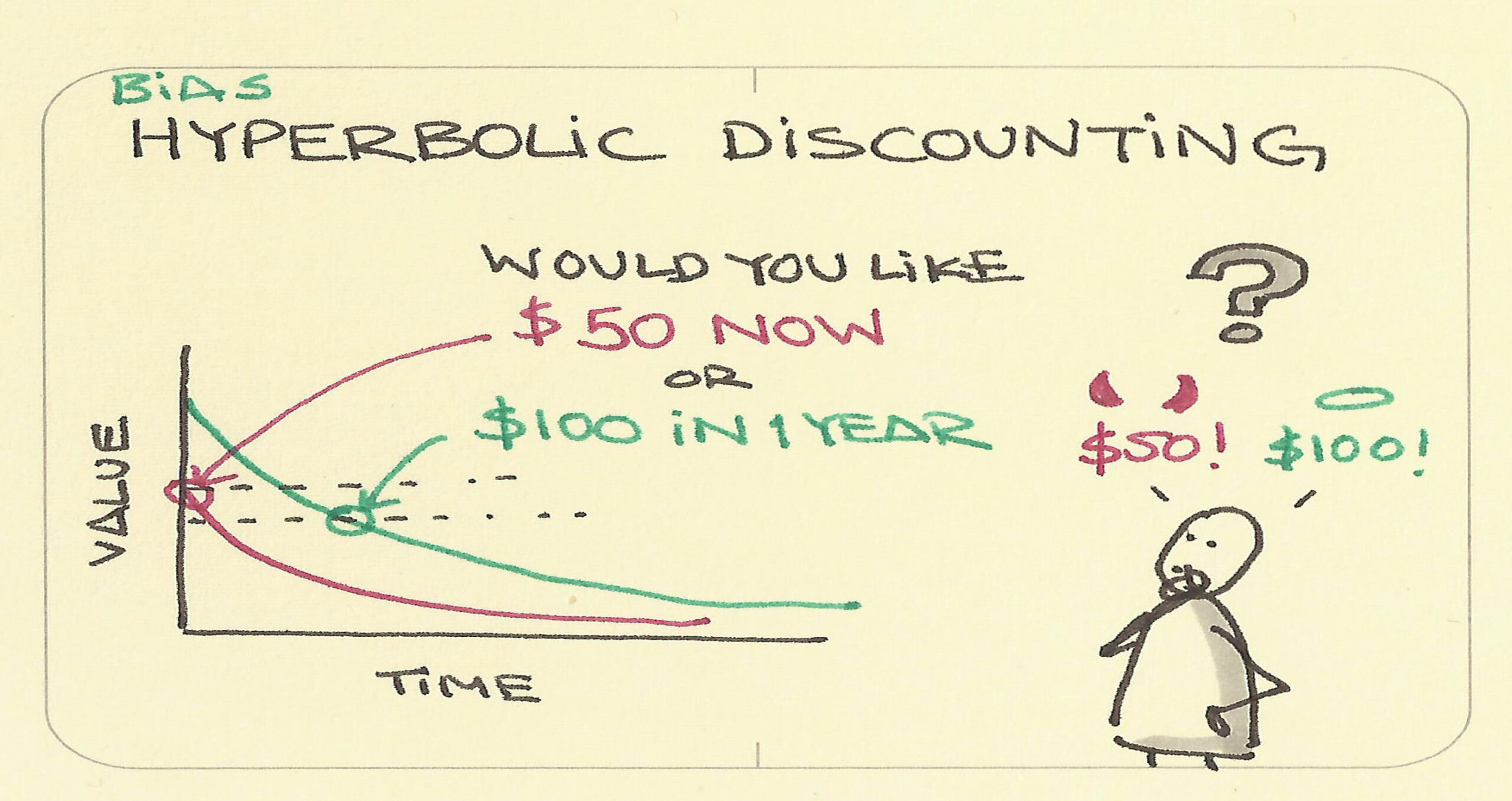
Hyperbolic discounting is a cognitive bias that involves individuals’ tendency to prefer smaller, immediate rewards over larger, delayed rewards, even when the delayed reward is objectively more beneficial. People often prioritize instant gratification over long-term benefits.
Explanations:
Hyperbolic discounting is related to the way our brains value rewards over time. The subjective value of a reward decreases dramatically as the delay increases, leading individuals to favor immediate satisfaction.
Examples:
Diet and Health: People may choose to indulge in unhealthy foods now, even when they know it is detrimental to their long-term health and weight management.
Savings and Investments: Individuals might prefer spending money on immediate purchases rather than saving or investing for future financial security.
Procrastination: Students may procrastinate on studying or assignments, opting for immediate leisure over long-term academic success.
Solutions:
Delayed Gratification Training: Practice delaying rewards and training yourself to be more patient, which can enhance your ability to make long-term decisions.
Goal Setting: Set clear long-term goals and break them into smaller, achievable milestones to maintain motivation.
Consequences Evaluation: Consider the potential negative consequences of prioritizing immediate rewards over long-term benefits.
Financial Planning: Develop a financial plan that includes saving and investing for the future to secure your long-term financial goals.
Addressing hyperbolic discounting involves recognizing the natural inclination to prioritize immediate rewards and actively promoting delayed gratification training, goal setting, consequences evaluation, and financial planning to make more balanced and informed decisions that consider long-term benefits.