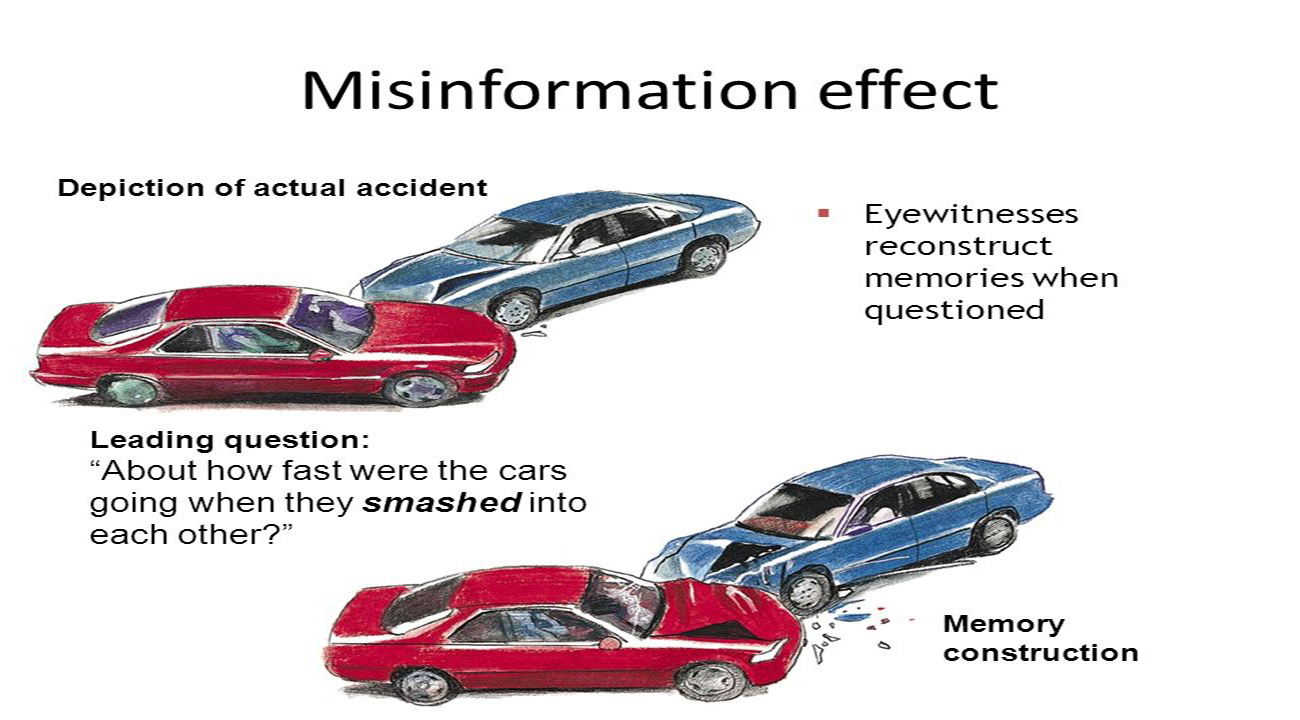
The misinformation effect is a cognitive bias that occurs when individuals are exposed to false or misleading information, which later influences their memory and recollection of an event, leading them to remember the event incorrectly. This bias illustrates how easily people can be swayed by erroneous information and misremember what actually happened.
Explanations:
The misinformation effect is related to the reconstructive nature of memory. When people are presented with false information, their memory can be altered, and they may unknowingly incorporate the misinformation into their recollection of events.
Examples:
Eyewitness Testimony: After being shown a misleading photograph or hearing false details from others, a witness may inaccurately remember a crime scene or suspect description.
News and Media: Exposure to incorrect or biased information in the media can lead people to remember events or facts incorrectly.
Leading Questions: During police interrogations or surveys, leading questions that contain false information can influence responses and later recollection.
Solutions:
Source Evaluation: Be critical of the sources of information and consider their credibility and potential biases before accepting information as true.
Corroboration: Seek multiple sources and perspectives to validate information and reduce the likelihood of misinformation influencing your memory.
Mindful Recall: Practice mindful recall and differentiate between facts you are sure of and details that might be influenced by external information.
Eyewitness Best Practices: Law enforcement agencies can adopt best practices to minimize the risk of the misinformation effect in eyewitness testimony.
Addressing the misinformation effect involves being aware of the potential for false or misleading information to alter one’s memory and recollection of events. By critically evaluating sources and practicing mindful recall, individuals can reduce the impact of this cognitive bias on their memories.