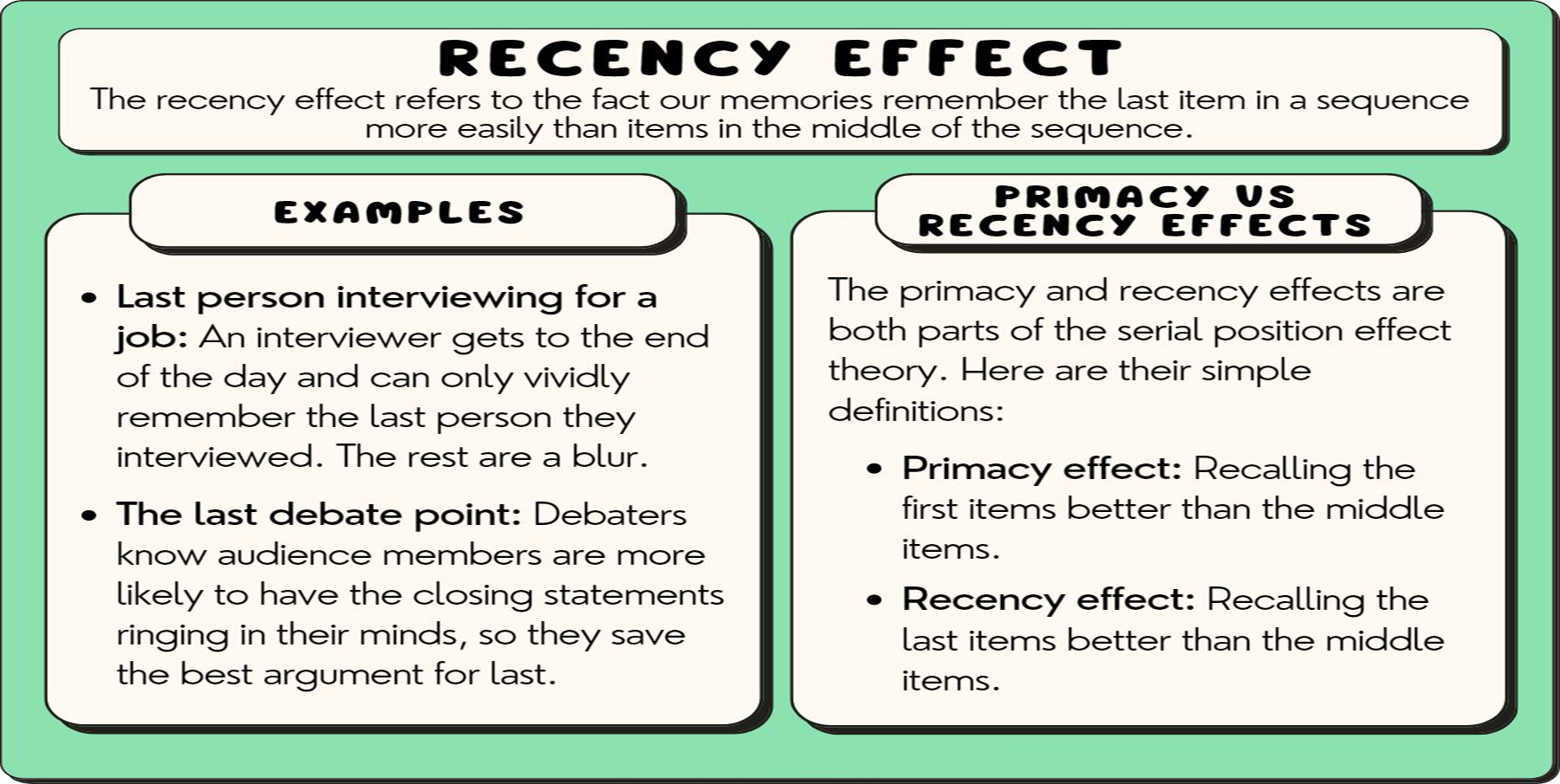
The recency effect is a cognitive bias that occurs when individuals have a stronger memory and better recall of items or events that occurred more recently compared to those that happened earlier. It often results in people overemphasizing the significance of recent information and downplaying the importance of earlier information.
Explanations:
The recency effect is linked to the way memory works, as well as the limited capacity of short-term memory. Information that is more recent is still readily available in short-term memory and tends to overshadow older information.
Examples:
Job Interviews: A hiring manager may be more influenced by a candidate’s final interview performance rather than their overall qualifications.
Product Reviews: Consumers may give more weight to recent product reviews when making purchasing decisions, overlooking older reviews.
Stock Market: Investors might focus on recent stock price fluctuations and trends while disregarding longer-term performance.
Solutions:
Long-Term Perspective: Encourage a long-term perspective and consider both recent and historical data when making decisions.
Journaling or Note-Taking: Keep records or notes to track important information and trends over time, which can counteract the recency effect.
Critical Thinking: Train yourself to critically evaluate the importance of recent information within the broader context of the situation.
Decision-Making Frameworks: Implement decision-making frameworks that incorporate both recent and historical data to provide a more balanced perspective.
Addressing the recency effect involves recognizing the natural inclination to prioritize recent information and consciously working to evaluate it within the context of historical data and trends. By adopting a more balanced perspective, individuals can make more informed decisions and reduce the impact of this cognitive bias.