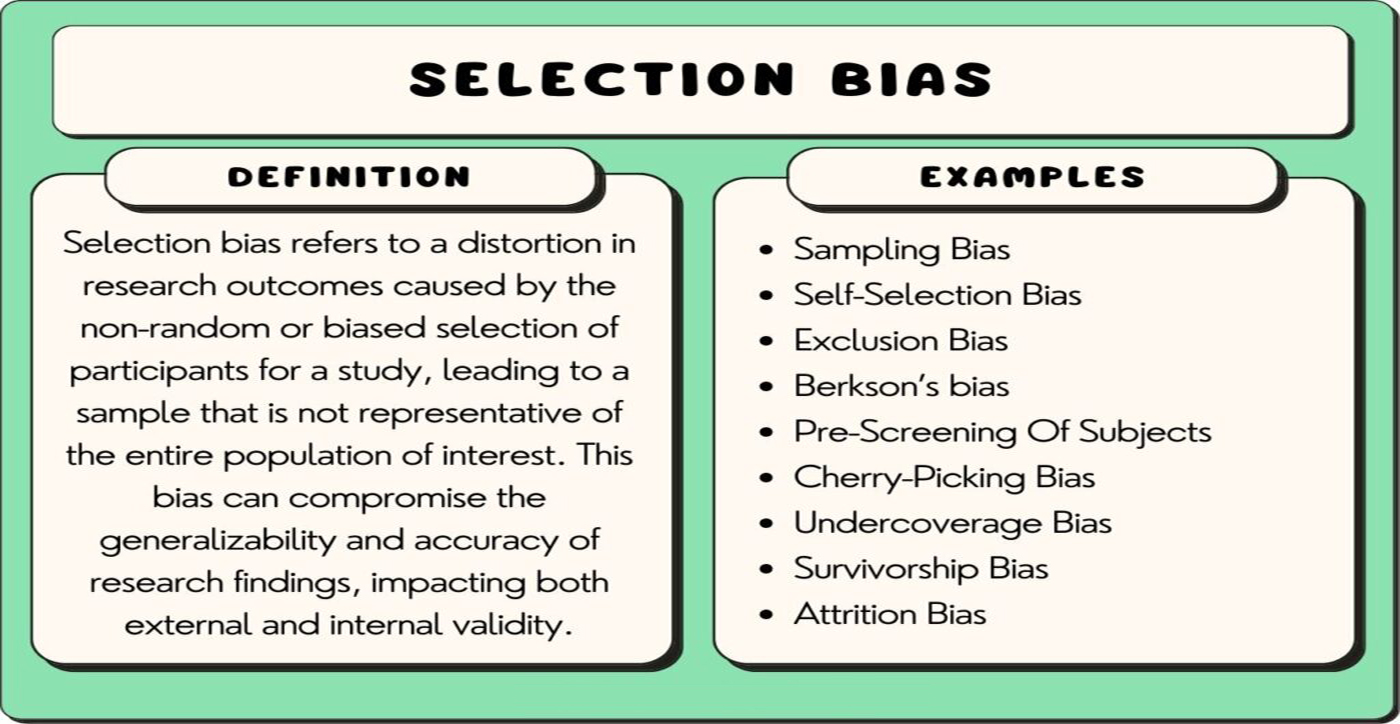
Selection bias is a cognitive bias that occurs when the data or information you collect is not representative of the larger population or sample, leading to inaccurate conclusions or generalizations. It is a common issue in research, decision-making, and everyday judgments.
Explanations:
Selection bias can arise from various factors, including the way data is collected, the criteria for selecting participants or data points, and the exclusion of certain information. It can lead to skewed results and incorrect assumptions.
Examples:
Medical Research: If a clinical trial for a new drug only includes healthy participants, the results may not accurately represent the drug’s effectiveness in the broader population, including those with health conditions.
Job Interviews: If a hiring manager only interviews candidates who were recommended by current employees, the sample may not reflect the full range of potential candidates, leading to limited diversity in the workforce.
Media Consumption: If you base your understanding of a particular topic solely on one news source, you may be exposed to a biased selection of information that does not represent the full spectrum of views or facts.
Solutions:
Random Sampling: In research and data collection, use random sampling methods to ensure that the sample is representative of the larger population.
Be Aware of Biases: Be conscious of the potential for selection bias in various aspects of decision-making and problem-solving. Question the representativeness of the information you have.
Cross-Check Sources: When gathering information or making decisions, consult multiple sources and perspectives to ensure a more balanced and comprehensive view.
Transparency: In research and data reporting, be transparent about the methods used to collect and select data. This can help others assess the potential for selection bias.
Addressing selection bias involves being aware of the potential pitfalls in your data collection methods and making a concerted effort to obtain a more representative and accurate sample.