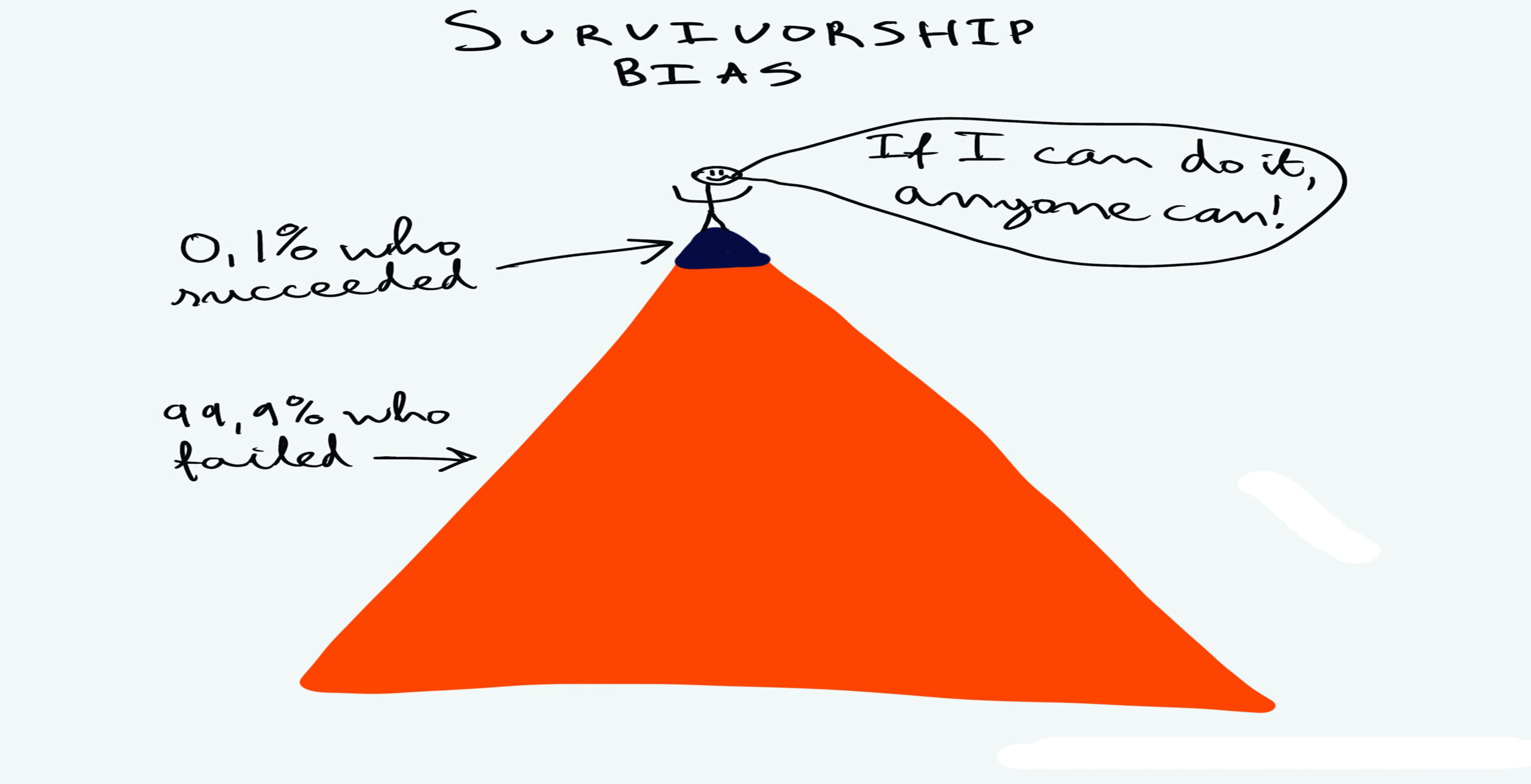
Survivorship bias is a cognitive bias that occurs when individuals focus on the success or survival of a particular group or entity, while ignoring the failures or non-survivors. It leads people to draw conclusions based on a biased sample that excludes those who did not succeed or survive.
Explanations:
Survivorship bias arises from the natural tendency to pay more attention to and learn from success stories, often neglecting to consider those who failed. It can distort one’s perception of the likelihood of success in various endeavors.
Examples:
Investment Advice: A person might exclusively study the investments that succeeded and overlook those that failed, leading to an inaccurate understanding of investment risks.
Business Strategy: Entrepreneurs may study only successful businesses and overlook the challenges and pitfalls faced by failed startups.
Self-Help Books: People might read self-help books or autobiographies of successful individuals without considering the struggles and failures that others faced.
Solutions:
Comprehensive Analysis: Consider both successful and unsuccessful cases when making decisions, especially in areas like investments, business, and personal development.
Learn from Failures: Study failures and learn from the mistakes and challenges faced by others to make more informed decisions.
Critical Thinking: Encourage critical thinking and skepticism when evaluating the advice and lessons offered in success stories.
Holistic Perspective: Emphasize the importance of examining the full range of experiences and outcomes in various fields.
Addressing survivorship bias involves recognizing the inclination to focus on success stories and actively promoting comprehensive analysis, learning from failures, critical thinking, and a holistic perspective to make more informed and balanced decisions.