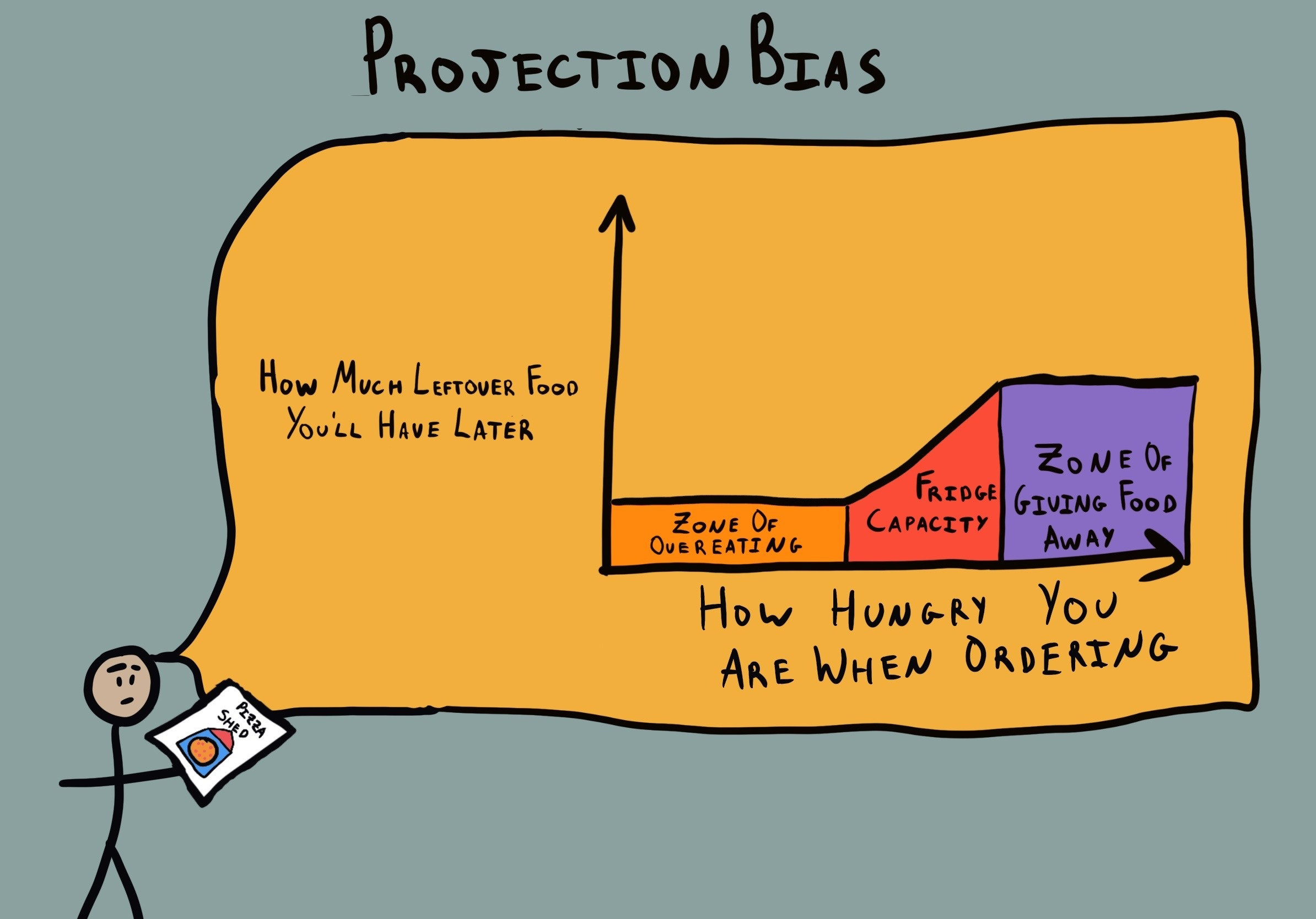
Projection bias is a cognitive bias that occurs when individuals assume that others share their beliefs, values, or feelings. People often project their own thoughts and emotions onto others, believing that others see the world in the same way they do.
Explanations:
Projection bias is rooted in the challenge of understanding the perspectives of others, as individuals naturally interpret the world through their own experiences and emotions. It can lead to misunderstandings and miscommunication.
Examples:
Political Beliefs: A person with strong political beliefs might assume that everyone in their social circle or community shares the same political views.
Emotional States: Someone in a good mood might expect that others are also feeling happy and responsive, even when this is not the case.
Cultural Norms: An individual from a particular cultural background may project their cultural norms onto people from other cultures.
Solutions:
Empathy: Cultivate empathy and actively try to understand the perspectives and emotions of others.
Communication: Encourage open and honest communication to uncover the true beliefs and feelings of others.
Question Assumptions: Be aware of the tendency to project and question assumptions about what others think or feel.
Cultural Sensitivity: When interacting with individuals from different backgrounds, be mindful of cultural differences and avoid making assumptions.
Addressing projection bias involves recognizing the inclination to assume that others share one’s beliefs, values, or feelings and actively promoting empathy, open communication, questioning assumptions, and cultural sensitivity to better understand the perspectives of others.